Why is Africa a “have-not” in the Digital Divide?
22/09/2015Many people wonder as to why Africa lags so far behind on the internet stakes. Look at any infographic about “the most” internet users, highest penetration rates or e-commerce sales and you rarely see an African nation. Why?
The reason why is what is known as the digital divide.
The digital divide is a term used to describe apparent disparities that exist in the world over access to information and technology. This divide can be between say, the rich and poor in a country, or between countries themselves.
“The Digital Divide, or the digital split, is a social issue referring to the differing amount of information between those who have access to the Internet (specially broadband access) and those who do not have access.” (internetworldstats)
As well as access to internet, it is also important to recognise the digital divide also encompasses an inequality between people over access to Information
and Communication Technologies (ICT), i.e. they don’t even have the means to access information. The “have-nots” in this scenario are perceived to be disadvantaged in not being able to use the same tools and know the same things as the “haves”.
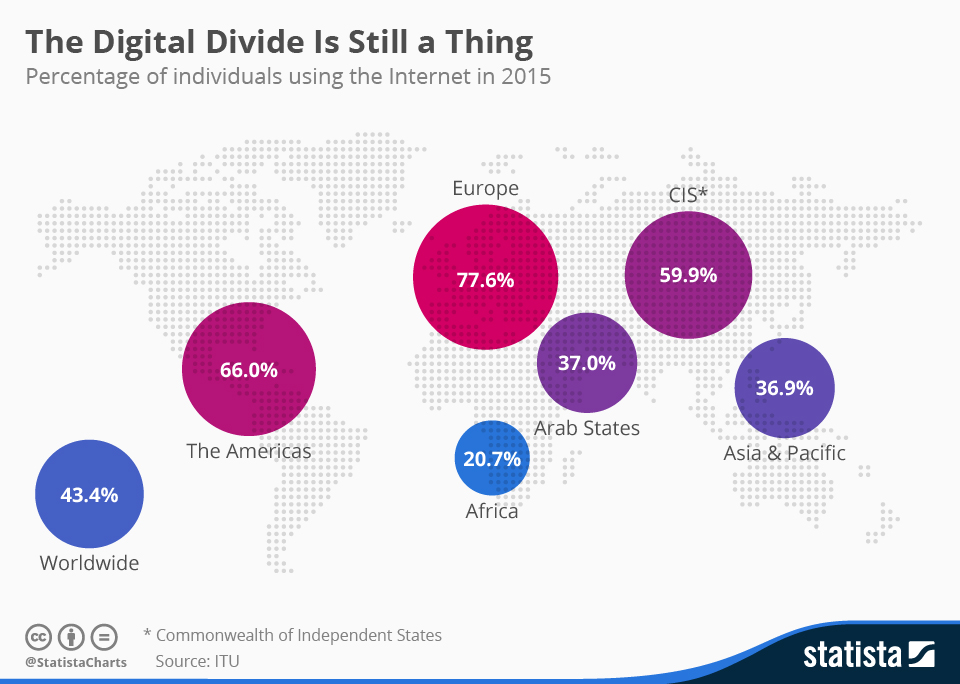
Africa, as we have said, on a global scale is definitely within the have-not camp. The infographic below from statista says it all.
Reasons for the Digital Divide in Africa
So why the digital divide? For those who have perhaps visited or done business in Africa, the reasons might be clear. For those with little first-hand knowledge, there are some rather fundamental reasons as to why Africa simply can’t deliver ICT and internet access as other continents. These include:
- Cost plays a big part in life decisions in Africa. Computers, iPhones and tablets all cost extortionate amounts of money. Without these computers, how can people access the internet?
- Even if someone saves up to buy a nice shiny second-hand laptop, they might not then be able to afford the prices for data or internet plans.
- Those living outside of cities struggle to get internet connections simply due to the lack of telecommunications infrastructure. No phone lines means no broadband.
- Power cuts are a part of everyday life for most Africans. Lack of power means you pretty much can’t do anything digital. And this is in the cities – many rural communities simply have no power!
- Most Africans were not educated in schools where computers or ICT were part of the curriculum. IT literacy is low although of course in the younger generation, the opposite is the case.
- The use foreign language across much ICT also prevents Africans from adopting and using it. The more things are localized into indigenous languages the more people might be willing to try it.
So, as you see, it’s really the basic fundamentals that are holding Africa back and causing the “digital divide”.